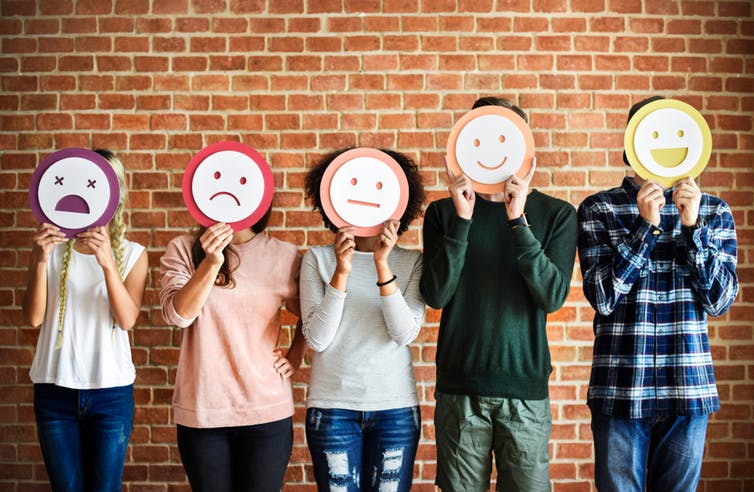
Emotional competence is an important life skill. Children with a high level of emotional competence, tend to have more friends, do better at school, and are more likely to help others.
Emotional competence has three components: understanding, expression and regulation. And these are all things parents can help their children to master. One way children can learn about emotions is by talking about them with their parents. So here are six phrases that could help with your child’s emotional development.
1. It’s OK to feel what you are feeling
Children and adolescents worry about not being “normal”, a feeling that stems from a need to fit in. To begin with, young children mostly want to fit in with their family. Then, as they grow, the need to fit in with their peers grows stronger.
By telling them that it’s OK to feel whatever it is they are feeling, we are normalising their emotions. We are telling them that there is nothing “weird” about them, and they fit in just fine.
2. How you feel right now won’t last forever
Emotions are not permanent, and children need to understand that feelings have a beginning and an end. Importantly, children should also learn that not only will an emotion pass, but that until that happens, its intensity will decrease.
By understanding this, children will be able to cope better with their emotions. This is especially important in the case of negative emotions, when the feeling of not being able to deal with them may lead to harmful behaviour.
3. Don’t let your feelings control you
Although we can’t totally control our emotions, we can to a large extent influence which emotions we have, when we experience them, and how we express them. This is called emotional regulation and is best achieved by changing the way we think about our feelings.
This is possible because the situations we face don’t automatically cause specific emotions. Instead, the emotions we feel depend on our evaluation of those situations. For example, a teenager applying for a summer job interview can view the experience as a pass/fail experience or as an opportunity to learn. It is the evaluation of the experience – something we can control – which will influence the way we feel about it.
4. Let’s put a name to your feeling
Children are not always able to name the feelings they experience. But it is important that we help children put a label on their emotions because by doing so they tend to feel better. Studies analysing adult brain activity show that by naming feelings of anger and sadness, the amygdala (the part of the brain that deals with emotions) becomes less active. This in turn reduces the intensity of our emotional responses and makes us feel better.
5. Why are you behaving this way? Let’s think about how you are feeling
Our behaviours stem from our emotions, so children need to understand the link between the two. By achieving this understanding, children are better able to predict and regulate their own behaviours and the behaviours of those around them.
For example, if a child knows that when he is angry with his brother he usually hits him. The next time this happens, he will be better equipped to regulate himself and not lash out.
6. No matter what you feel, I am here for you
This is perhaps the most important thing that we can tell our children to help them develop their emotional competence. Children experience many different emotions and some of them are accompanied by guilt or shame.
If, for example, a teenager falls in love with his best friend’s girlfriend, he may feel ashamed or guilty. By telling him that no matter what he feels we are there for him, he will feel secure enough to talk about those emotions, which in turn will help him to process them effectively, helping his overall mental health.
 Emotional times. Shutterstock/agsandrew
Emotional times. Shutterstock/agsandrew
Generally speaking, anything that helps parents and their children to discuss emotions is a positive step. The more we talk to young people about feelings, the more they will develop their emotional competence. By doing this, we will also be telling our children that we value them, that we are interested in them, and that we love them. These are the best kind of messages we can give our children – and ones that will make them feel strong.![]()
About The Author
Ana Aznar, Lecturer in Psychology, University of Winchester
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Related Books:
Here are 5 non-fiction books on parenting that are currently Best Sellers on Amazon.com:The Whole-Brain Child: 12 Revolutionary Strategies to Nurture Your Child's Developing Mind
by Daniel J. Siegel and Tina Payne Bryson
This book provides practical strategies for parents to help their children develop emotional intelligence, self-regulation, and resilience using insights from neuroscience.
Click for more info or to order
No-Drama Discipline: The Whole-Brain Way to Calm the Chaos and Nurture Your Child's Developing Mind
by Daniel J. Siegel and Tina Payne Bryson
The authors of The Whole-Brain Child offer guidance for parents to discipline their children in a way that promotes emotional regulation, problem-solving, and empathy.
Click for more info or to order
How to Talk So Kids Will Listen & Listen So Kids Will Talk
by Adele Faber and Elaine Mazlish
This classic book provides practical communication techniques for parents to connect with their children and foster cooperation and respect.
Click for more info or to order
The Montessori Toddler: A Parent's Guide to Raising a Curious and Responsible Human Being
by Simone Davies
This guide offers insights and strategies for parents to implement Montessori principles at home and foster their toddler's natural curiosity, independence, and love of learning.
Click for more info or to order
Peaceful Parent, Happy Kids: How to Stop Yelling and Start Connecting
by Dr. Laura Markham
This book offers practical guidance for parents to shift their mindset and communication style to foster connection, empathy, and cooperation with their children.

























